InvenioRDM v9.0¶
2022-05-24
Long-term support (LTS) release
We're happy to announce the release of InvenioRDM v9.0. The release is a long-term support release which is maintained until the next LTS release + 6 months (and minimum for 1 year).
Try it¶
What's new?¶
InvenioRDM v9.0 ships with the much anticipated communities feature! 🎉
Communities¶
Communities is a new core feature of InvenioRDM that empower users to self-organise and manage content in InvenioRDM. The feature launching has focused on two main use cases:
- Submit a record for review in a community
- Manage members of a community
This is only the beginning of the community feature and we're expecting to heavily expand the feature in the future.
Visibility: Public or restricted¶
Communities visibility can be set to either:
- public - any user can see the community
- restricted - only community members can see the community
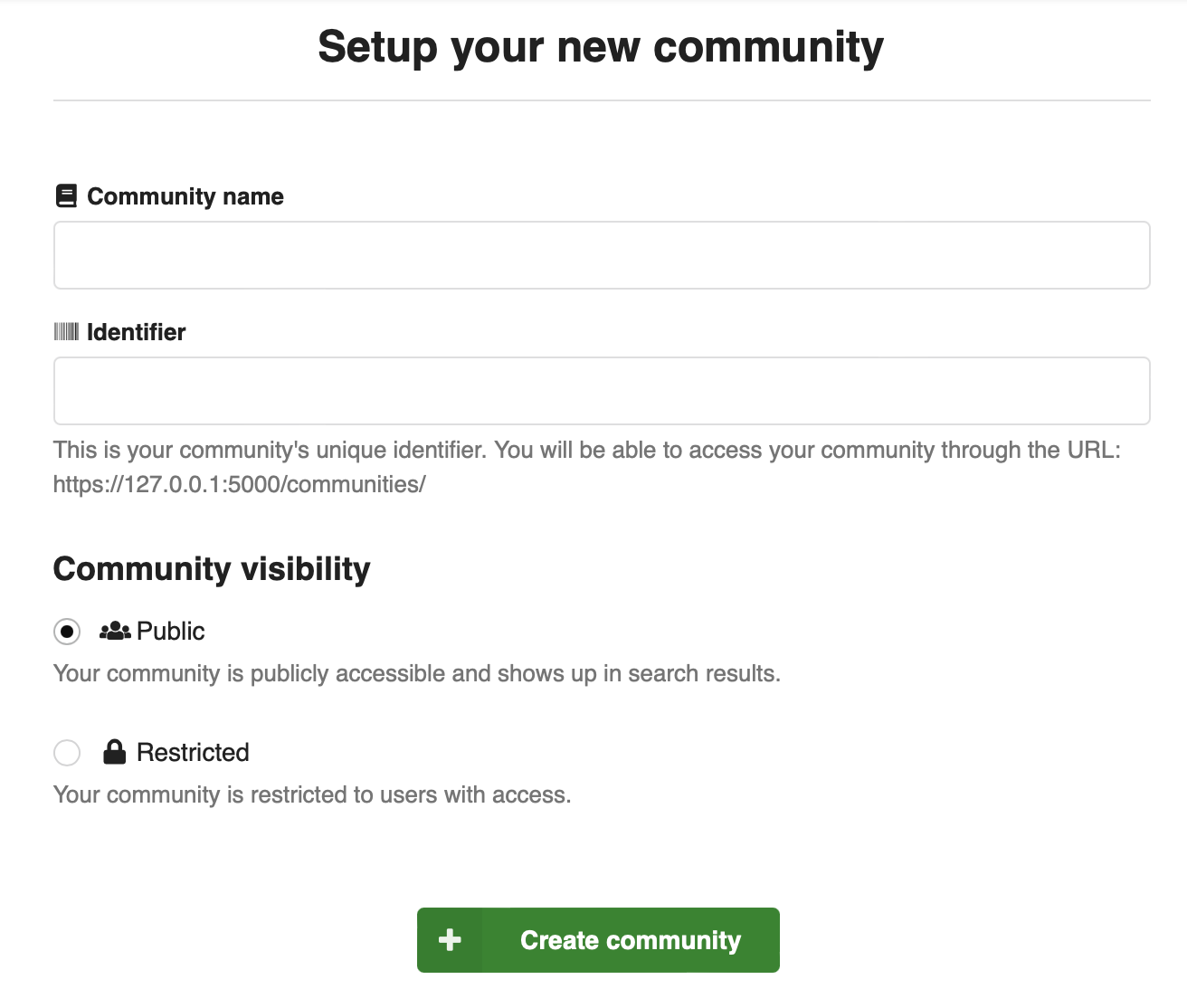
Both public and restricted communities can contain restricted records, and thus not all records in a public community may be visible to everyone. A restricted community on the other hand may only contain restricted records.
Records and branding¶
A community may co-own any number of records, and users can search through the records of the community:
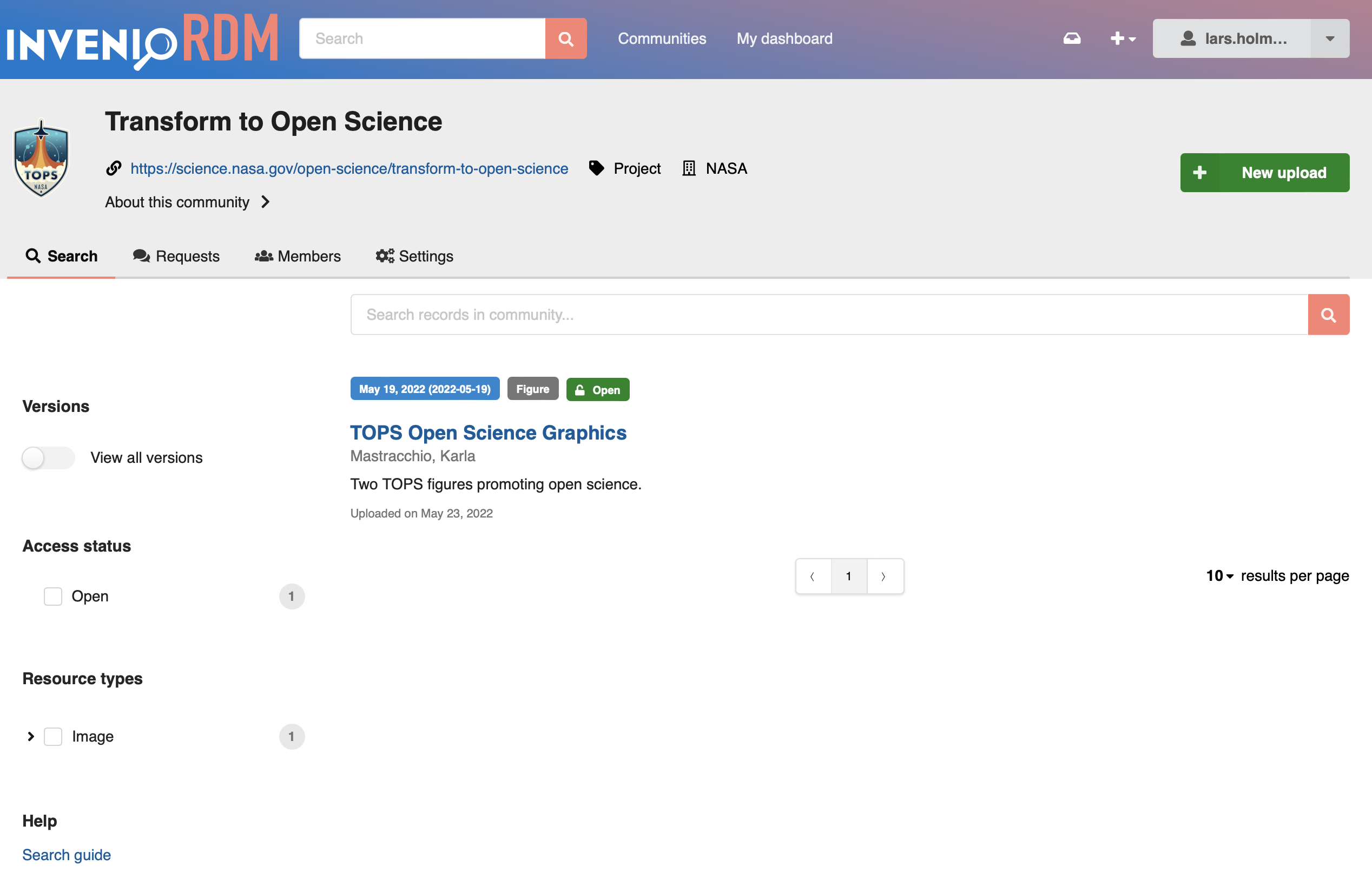
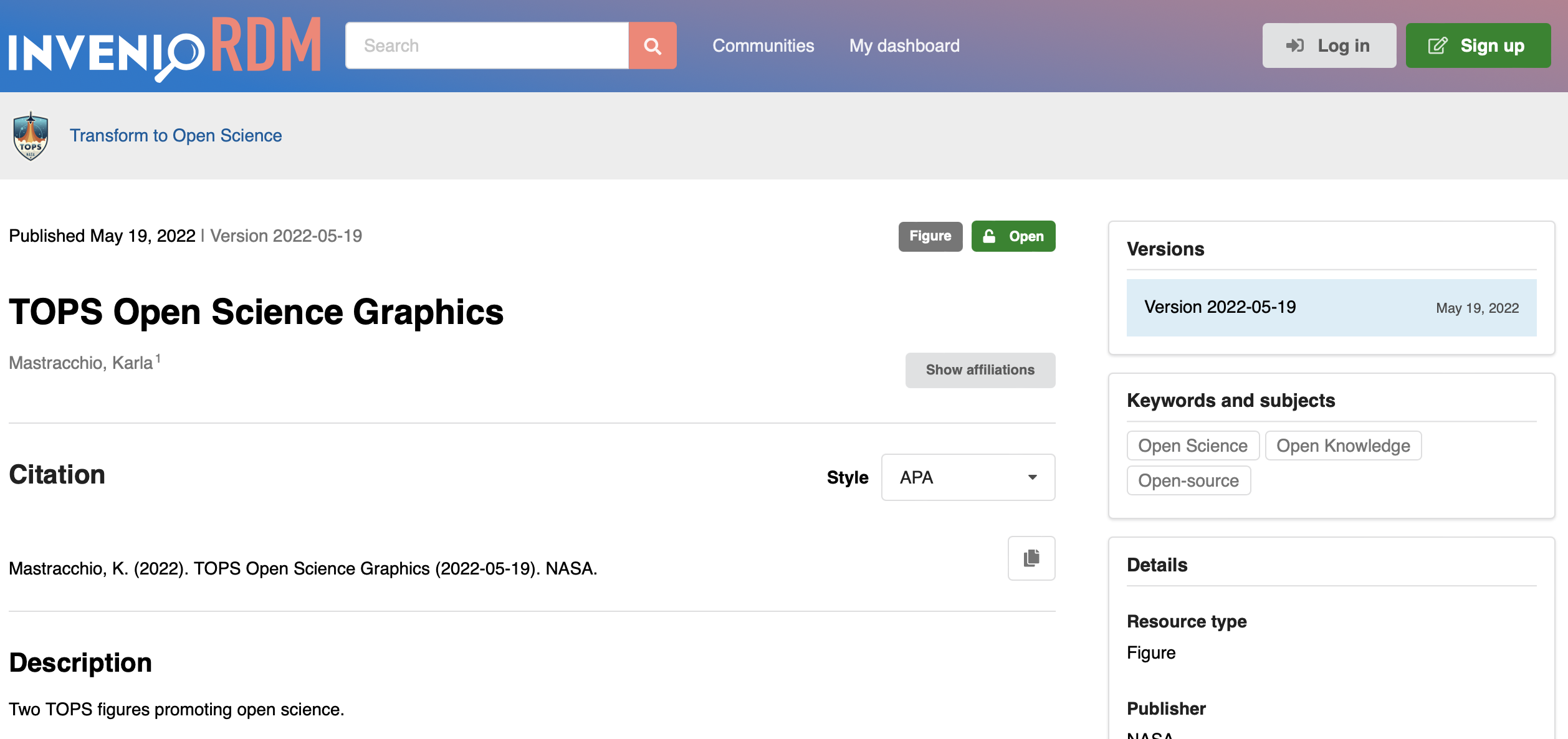
Records that are owned by a community are, by default, branded with the community as well:
Members¶
A community by default always has one or more owners, but you can invite multiple members to a community. Members can be either people or groups:
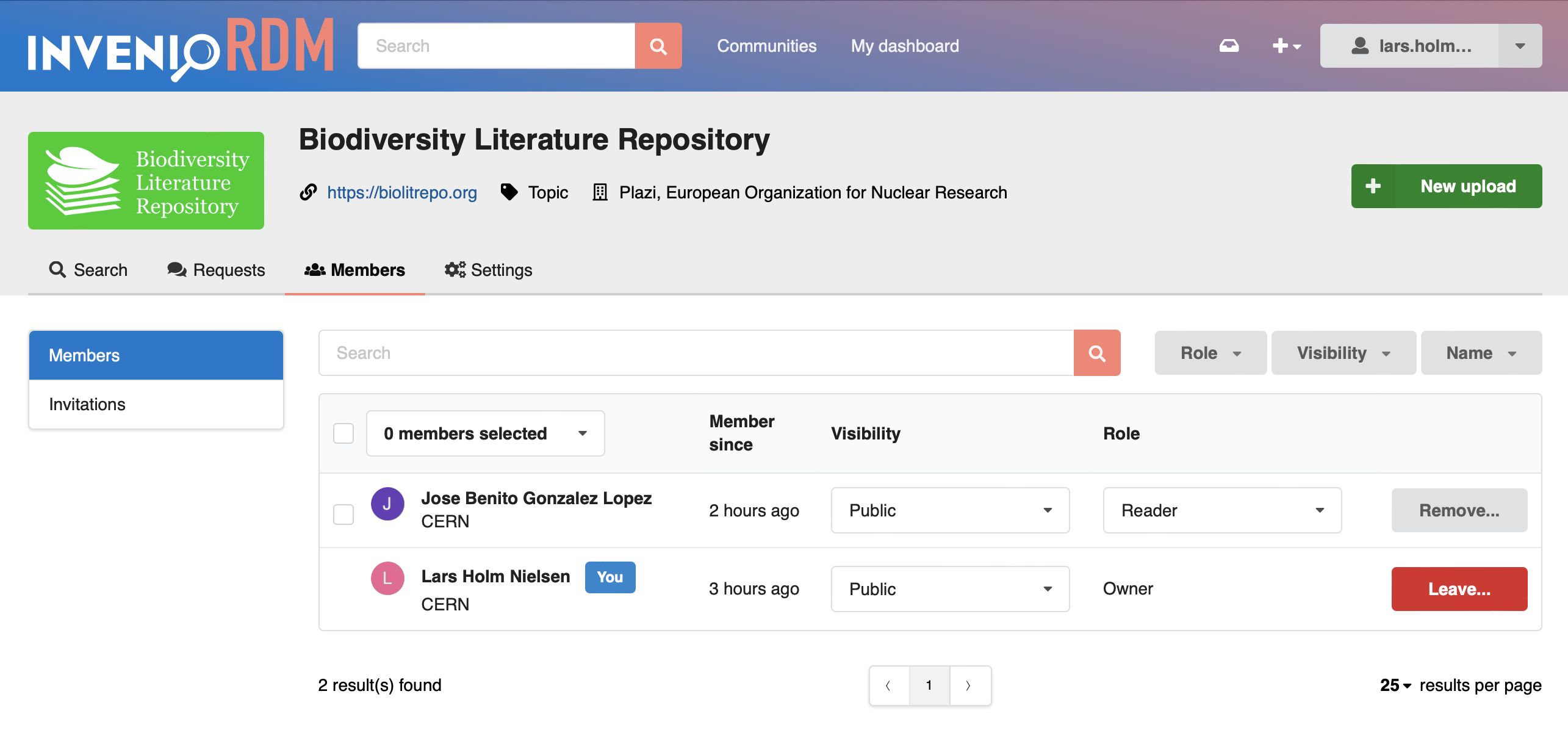
It's possible to disable support for group members via the COMMUNITIES_GROUPS_ENABLED
feature flag. See the groups
section to know how to integrate groups in your instance.
Roles¶
All community members have a role that determine what they are able to do within a community. By default InvenioRDM comes with the following roles:
- Reader: A reader is a member of the community and can view restricted records owned by the community.
- Curator: A curator can in addition to a reader also edit/accept/decline records in a community.
- Manager: A manager can in addition to curators also manage members of a community.
- Owner: An owner has full administrative access to a community, and can change all settings as well as delete the community.
The role definitions are configurable via the COMMUNITIES_ROLES configuration
variable. Thus, both titles and capabilities of the roles can be modified.
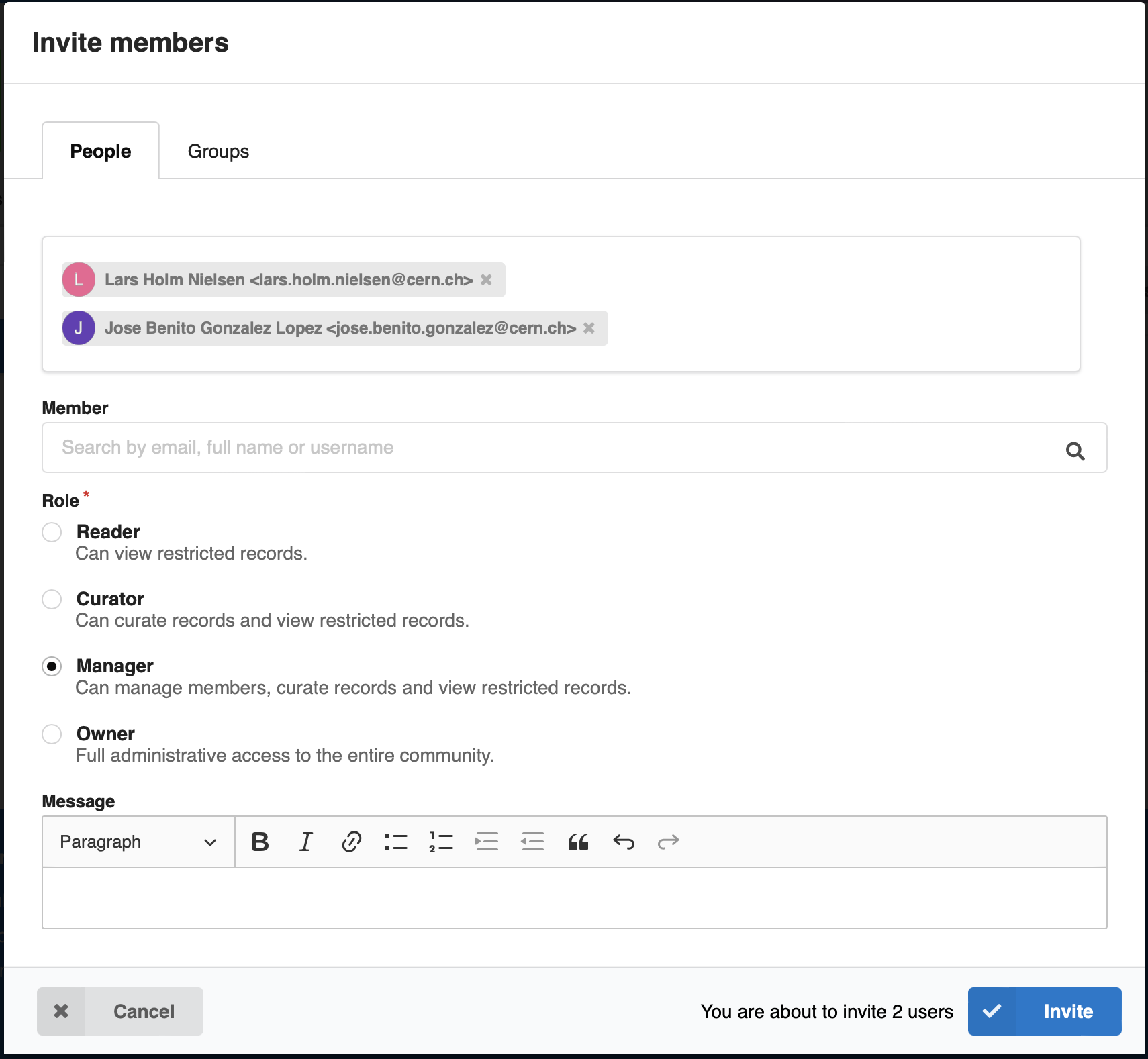
Member invitations¶
Owners and managers can invite other users to join the community. Groups can be added directly as a member of the community:
The invited user can accept/decline the invitation and in addition have a conversation with the sender of the invitation:
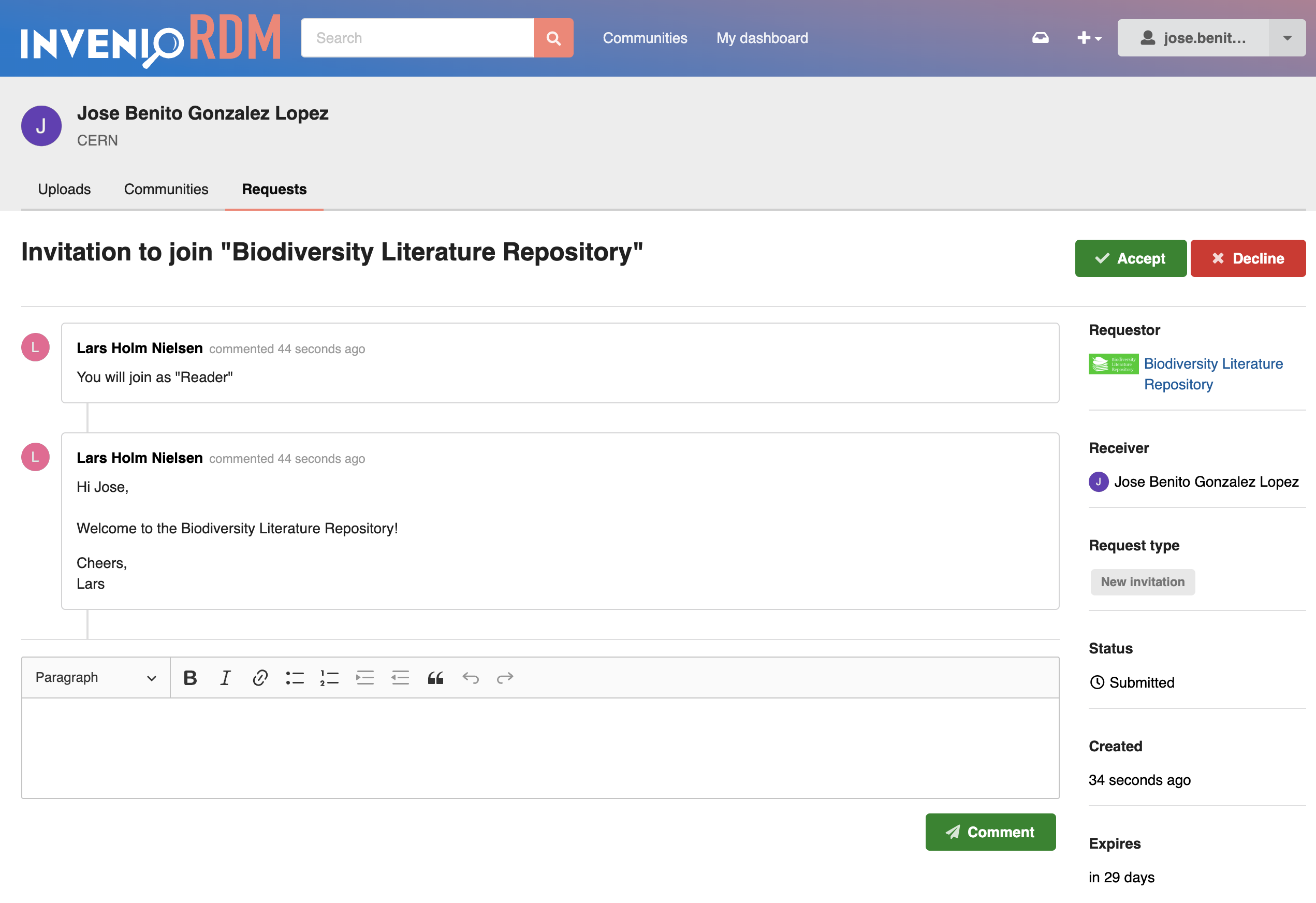
By default invitations automatically expire after 30 days and become invalid.
Reviews¶
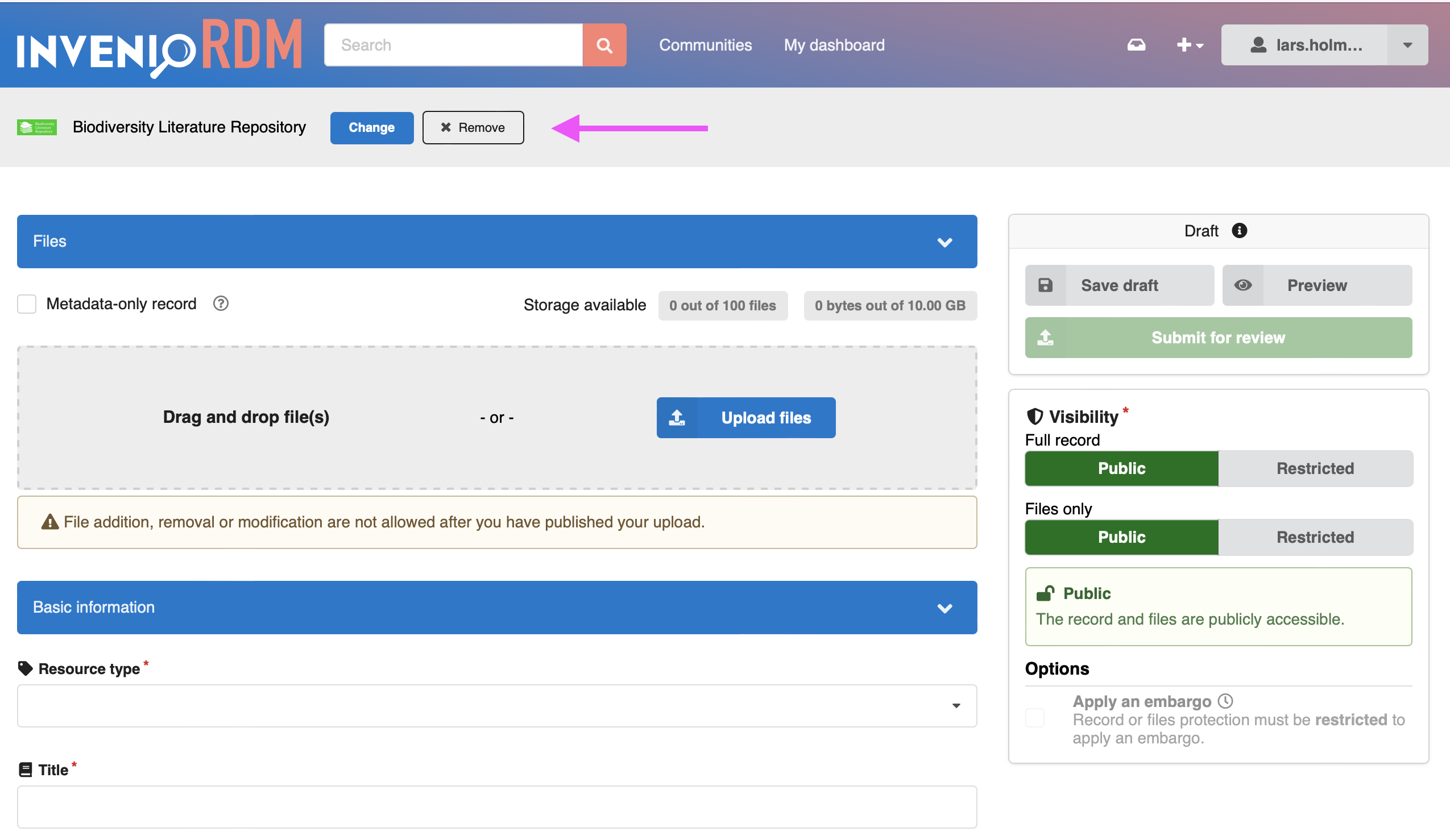
Any user can submit records to public communities for review:
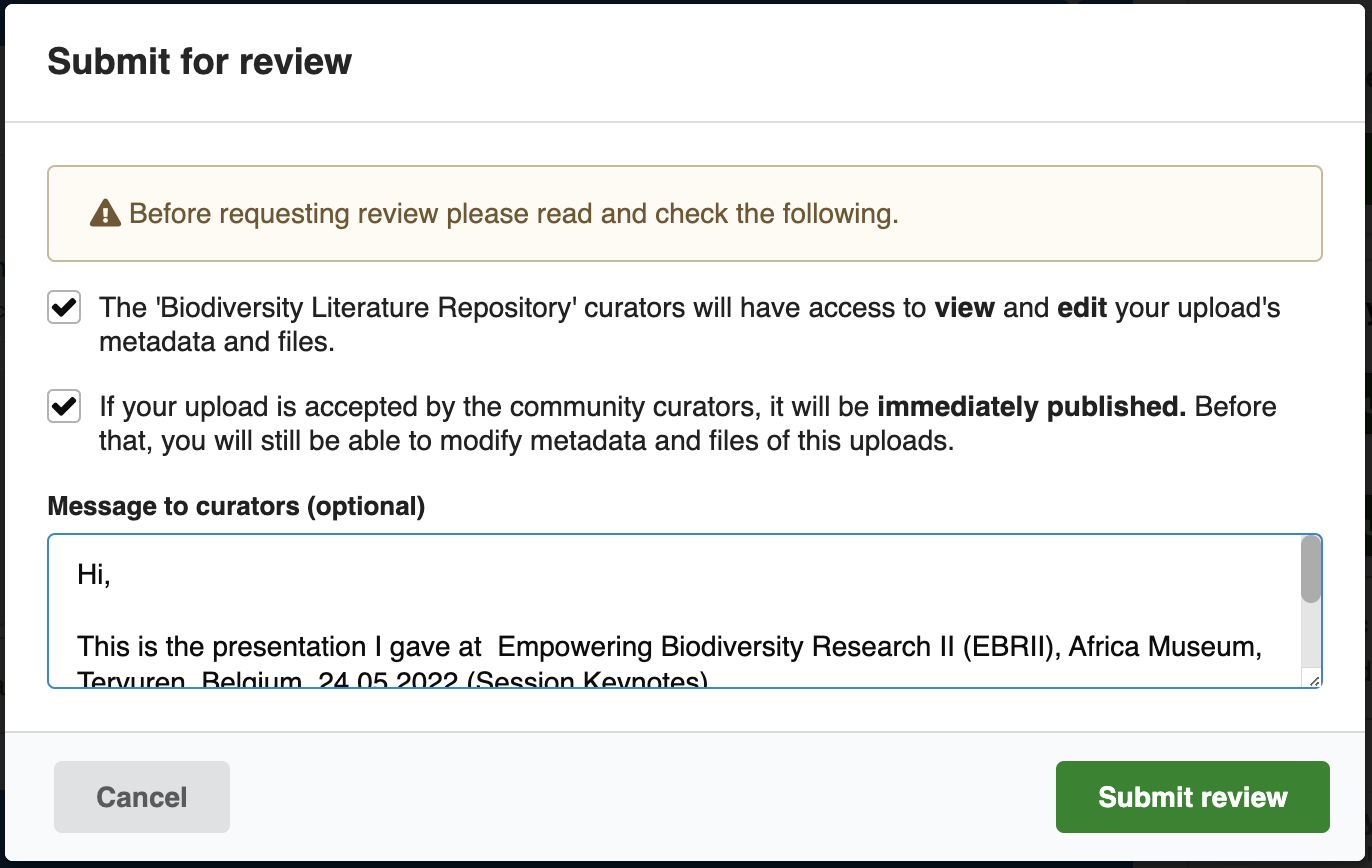
At submission time, a message can also be provided to the community curators:
Curation
Curators of the community will receive the review request under the new "Requests" tab, and can have a conversation with the submitter, as well as preview the submitted record. Both the submitter and curator can edit and update the record under review until it's published. Once published the record is owned by both the submitter and the community:
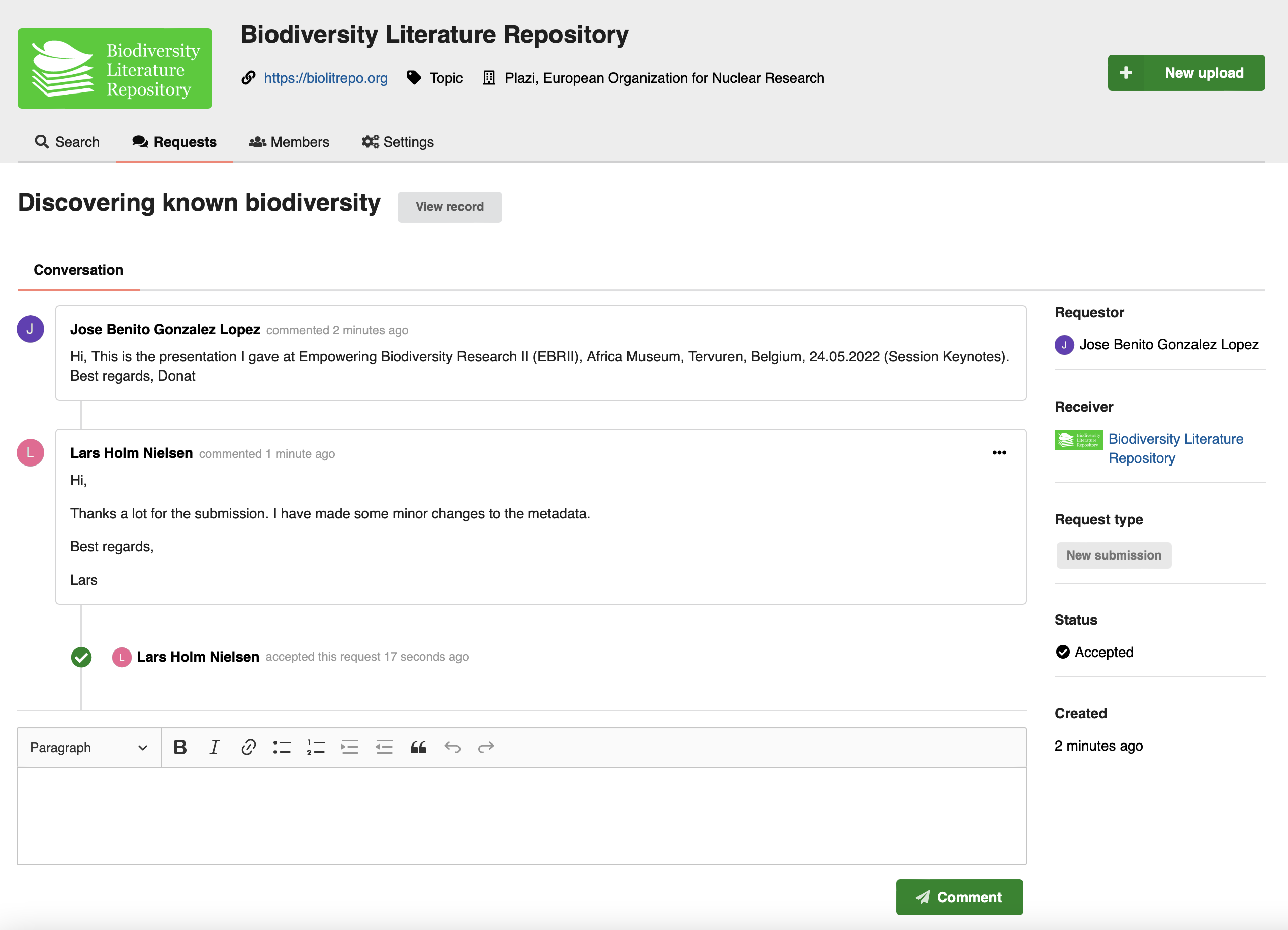
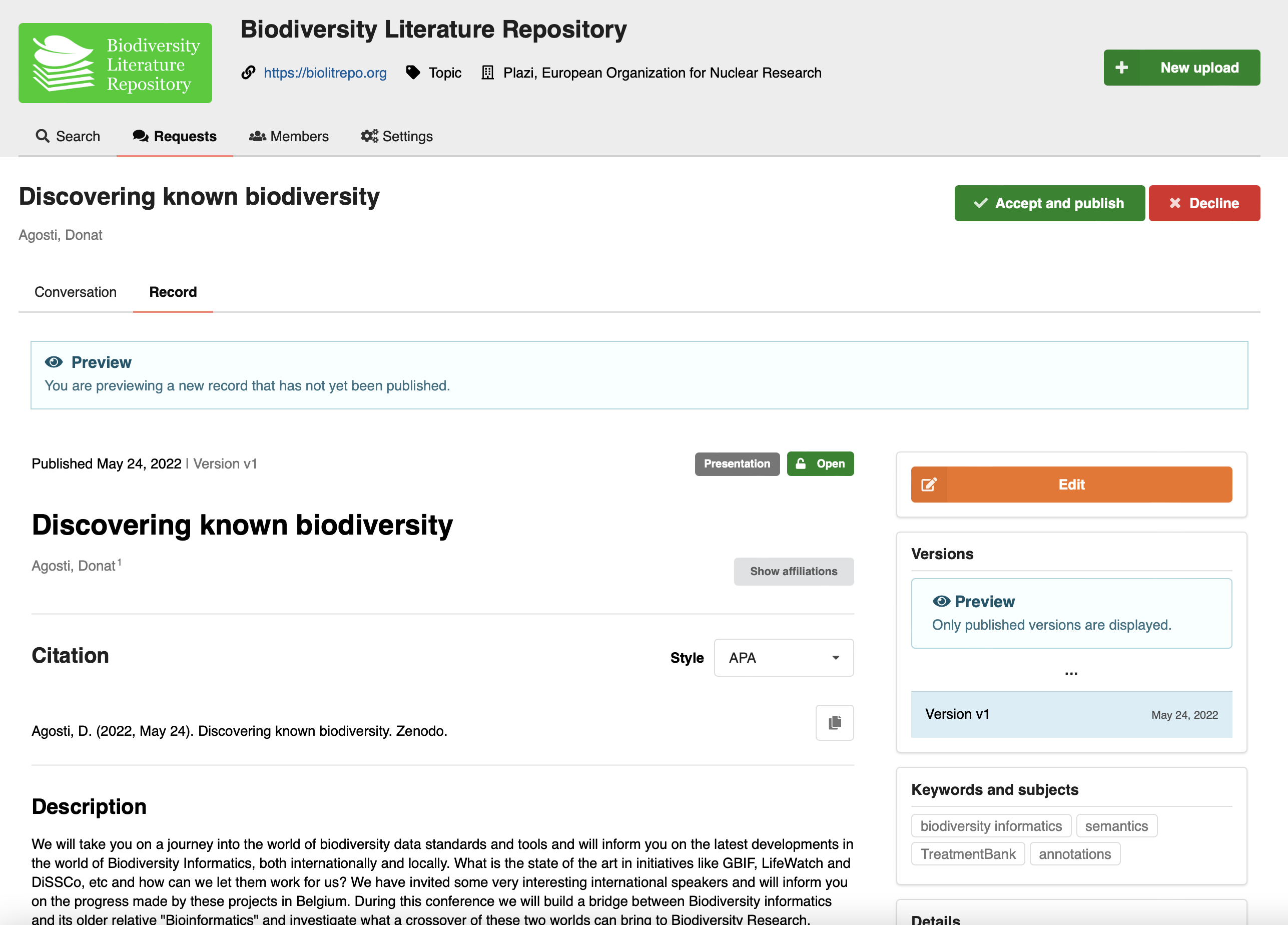
See also the Reviews REST API documentation.
Backend¶
You may have noticed that both invitations and reviews look similar and enable a conversation between a submitter and receiver of the request as well as allowing them to perform certain actions like accept/decline/cancel/expire.
The backend of this new feature is our new powerful requests module. The module enables us to more easily build new automated workflows in the future. Some of the new request types we're expecting to see in the future includes:
- File replacement
- Record removal
- Ownership transfers
- Quota increases
- Access requests
- Record claiming
Overall, the new backend is a key enabler for automating as much as possible standard requests that requires some sort of human approval. We are also looking forward to expand the requests module with assignees and status checks that could be updated from externally running workflows.
See documentation on the requests architecture.
Limitations¶
This is the very first release of the communities module, and thus also the current implementation have some key limitations that we're working to address as fast as possible. We've listed below the most important limitations:
-
Email notifications: There is no notification mechanism, and thus no emails or similar are sent for new requests. Users must go to their dashboard, or community requests, to see if there's any new requests or new messages.
-
Add to community after publish: If you publish directly, and later want to add a record to a community there's currently no way for the submitter or community curators to submit or claim records.
-
Removal from community: Once a record is accepted into a community, there is no user interface for removing the record from the community again. It's possible to programmatically remove records from a community.
-
Featured communities: A REST API exists for managing featured communities however there is no user interface on top of it yet.
-
Community logos and avatars: The current implementation of community logos requires extra work and design in order to better present a community.
-
Community search vs global search: Currently we have two search fields, one in the header to search all records, and one separate on the community search for records in the community. We want to integrate both of them into a single search field in the header.
Users, groups and profiles¶
In v9 we have also revamp the user registration and user profiles support. InvenioRDM now has basic support for customizable user profiles and preferences. In addition we have expanded the default user profile to include an affiliations field as well. You'll notice the new profile and preferences field in multiple ways.
First, the user registration form now shows more fields in addition to email and password, namely:
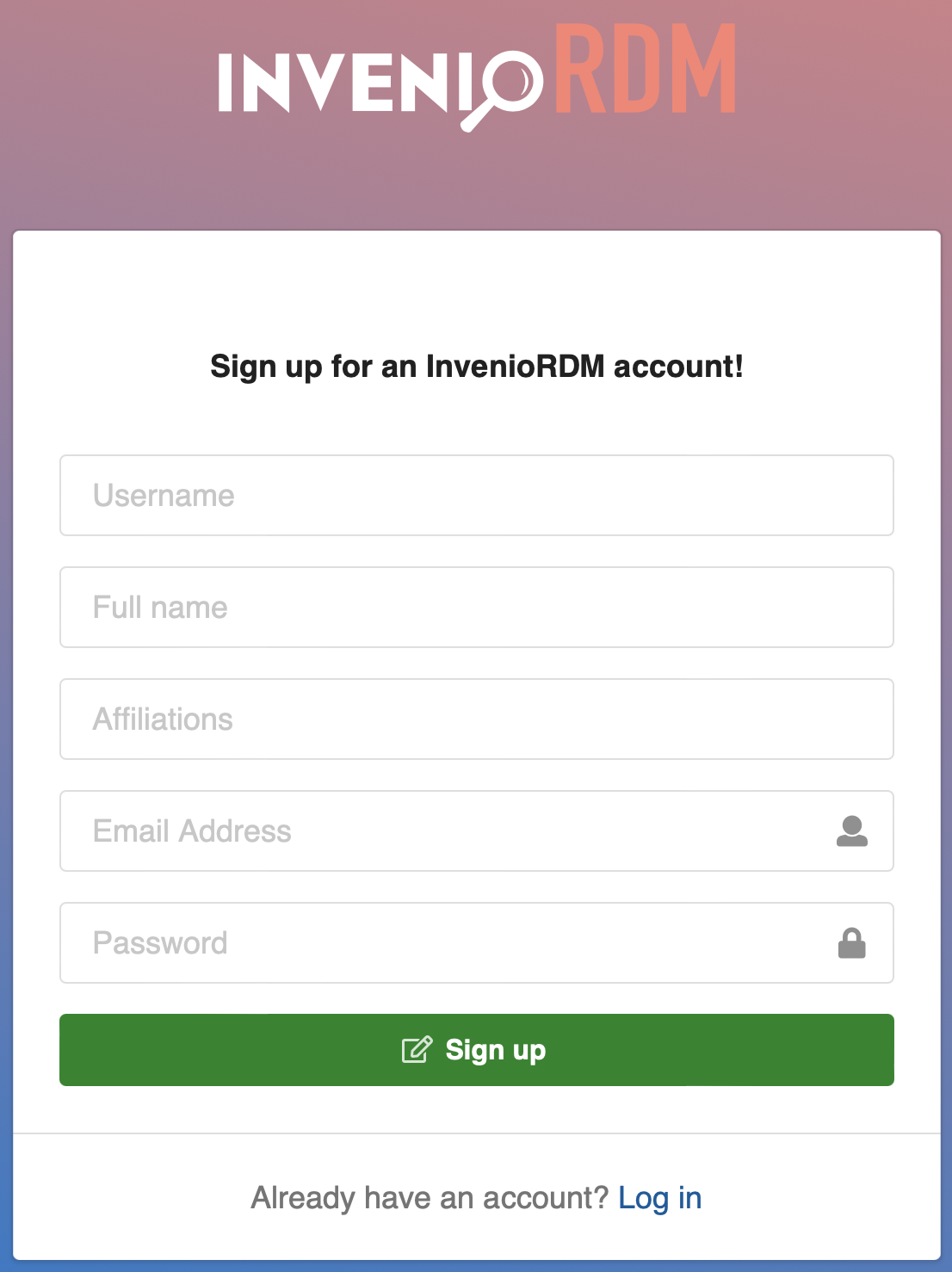
On the user's account settings page the new fields as well as the user preferences field will be displayed:
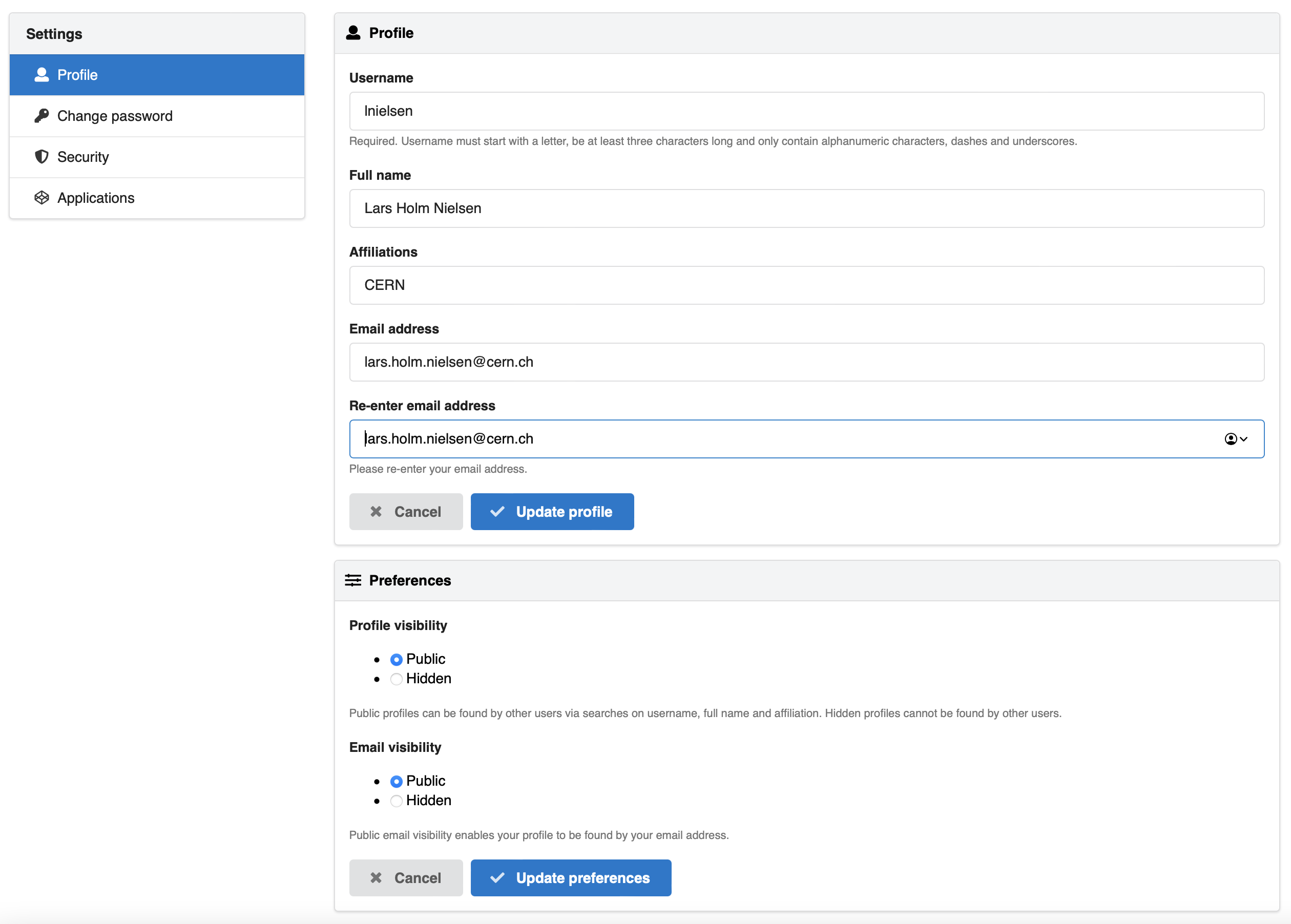
User preferences
The user preferences has currently two options:
- Profile visibility
- Email visibility
The options allow a user to control if they can be found by other users of the system by their profile information. By default, a user must explicitly enable the profile/email visibility in order to be found. If users are automatically created (e.g. from an institutional identity management solution), the system can automatically set these preferences for the user on creation.
Avatars
Users and groups now also have basic avatars. The avatars are created by taking a letter from the full name, username or email and compute a color for the user:
![]()
In the future, the idea is to support user uploaded avatars, identicons and online avatar services.
Verified email required for login
A user is now required to confirm their email address via a link sent to their email address in order to be able to login. The previous behavior of v8.0 and earlier can be reenabled by setting the following configuration variable:
SECURITY_LOGIN_WITHOUT_CONFIRMATION = True
Note, that for a user to be findable by other users, they must have verified their email address and set their profile visibility to public.
Users and groups REST API
InvenioRDM comes with a complete new REST APIs for users and groups search. The REST API powers for instance the member search when inviting new members to a community:
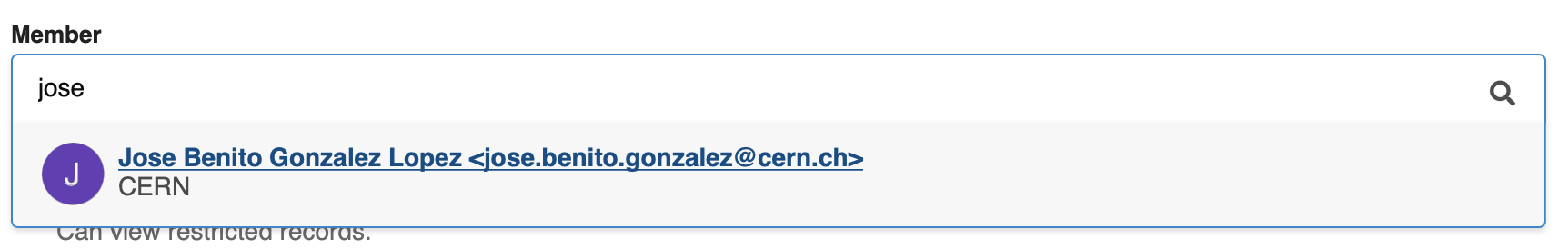
The REST API is currently limited to search, but will be extended in the future to also support creation and management of users and groups.
Backend changes
A significant fraction of the new features outlined above is enabled by some larger changes to the backend. User and groups are now indexed in the search cluster and thus we have separate profile information from e.g. login information and added features for tracking changes to users.
Also, we've moved a database table from Invenio-OAuthclient tracking external user identities to Invenio-Accounts. All of these changes are handled automatically by the upgrade procedures.
Funders and awards¶
We have added support for adding funding information to both records and communities:
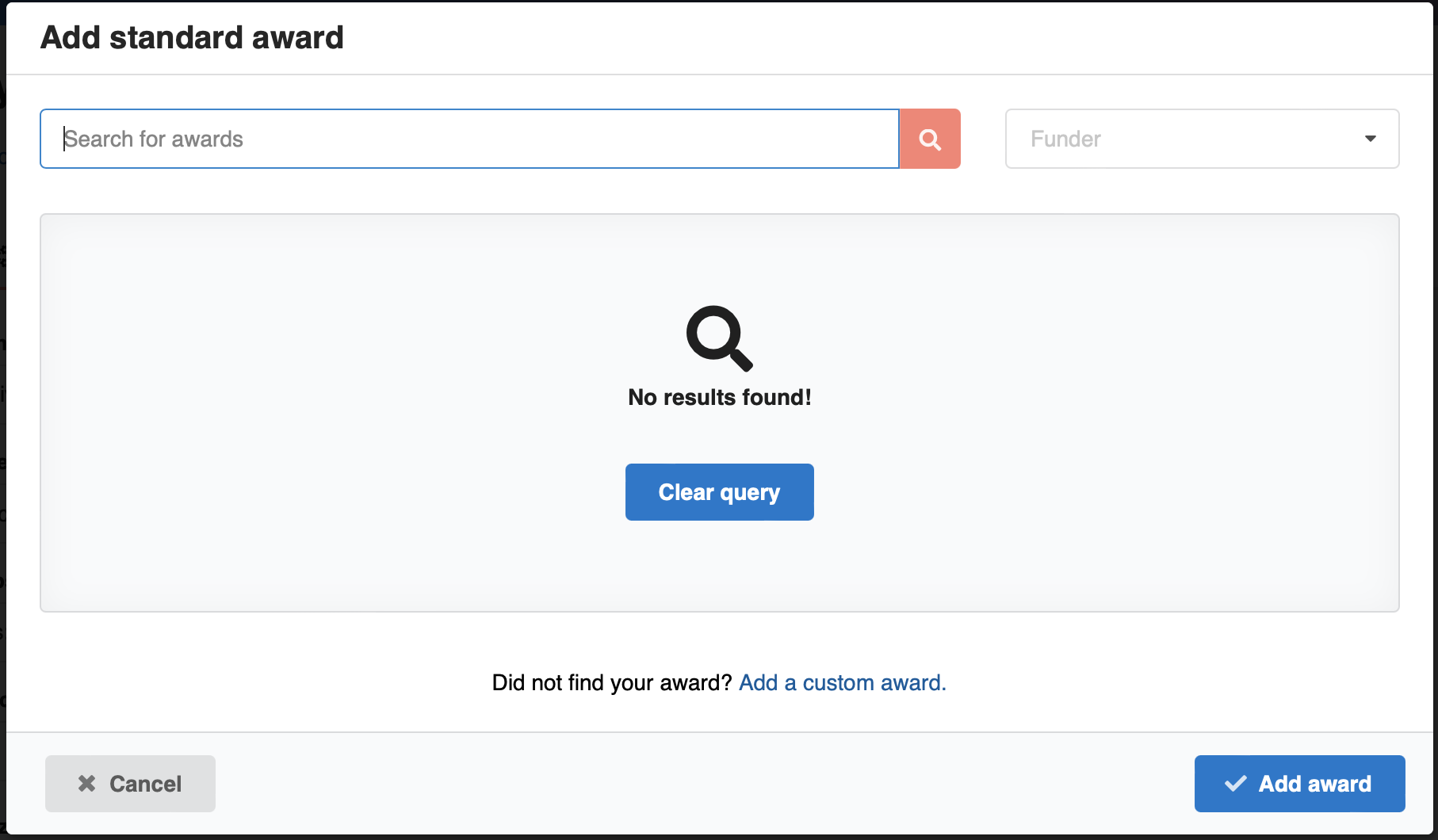
You can either search the funders/awards database for an existing award or add a custom award:
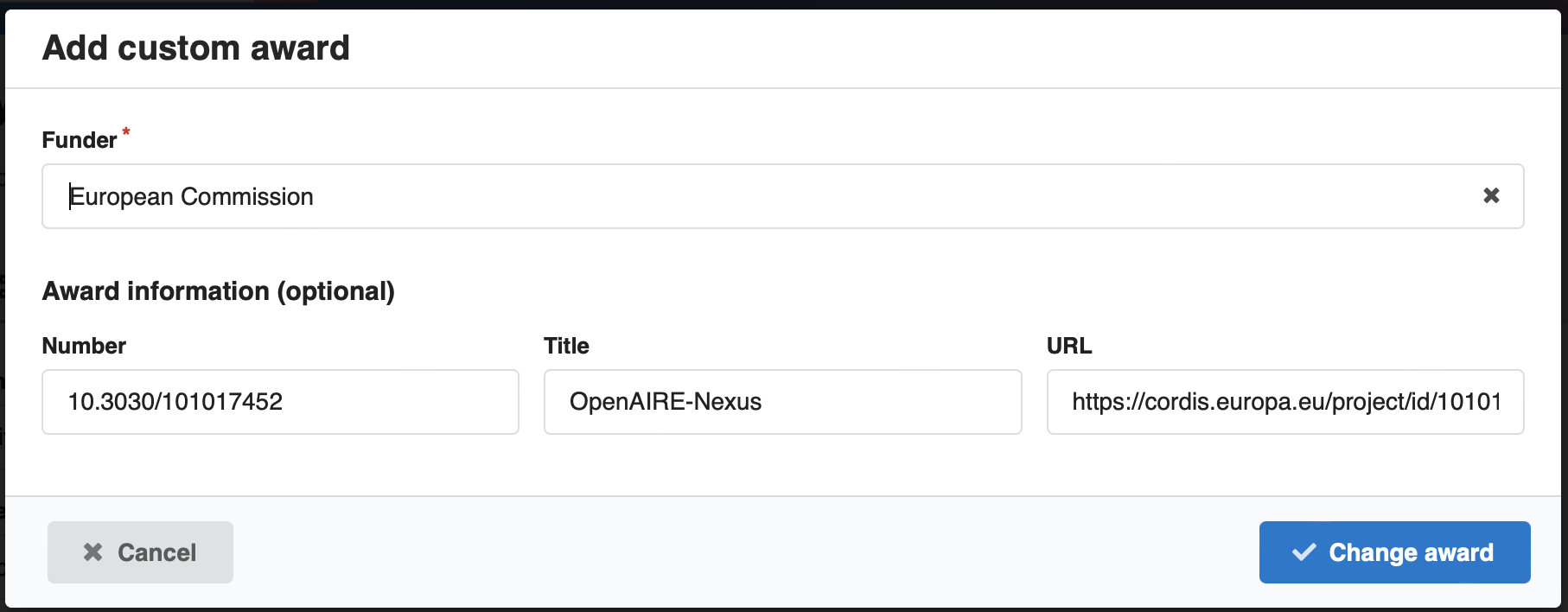
The features is driven by the underlying funder and award vocabulary. Both vocabularies can be loaded with data according to your organisational needs. You could for instance decide to load CrossRef Funder Registry or ROR into the funder vocabulary, and the awards vocabulary could be loaded from the OpenAIRE grants database.
See the Funder and Award vocabularies documentation for further details.
User Experience (UX) improvements¶
We have made a number of smaller UX improvements.
Light background on array fields
Array fields in the deposit form (e.g. dates, related identifiers) now have a light grey background around the group of fields for a single entry. This makes it easier to see which fields belongs together (especially in mobile/tablet views):
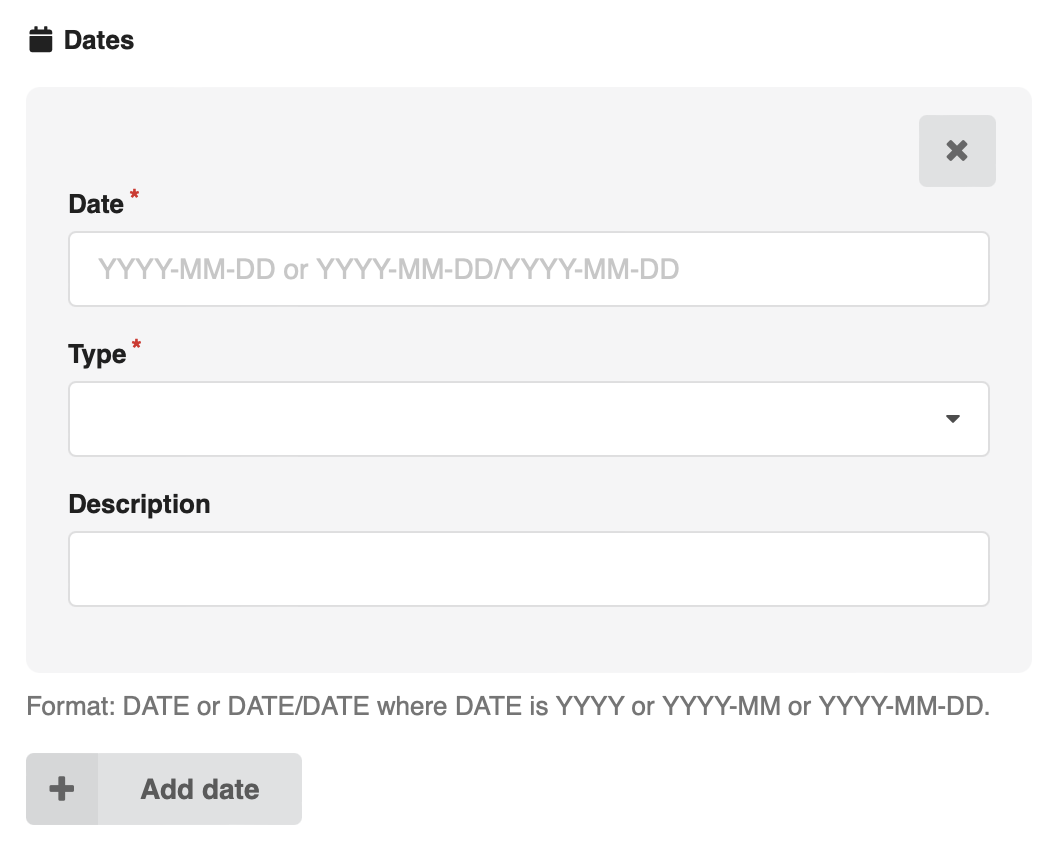
Responsive design and screen real estate
We've now managed to fix responsive design issues on most pages in InvenioRDM and thus pages work in both desktop, tablet and mobile browsers. This has also meant that e.g. the deposit form and record landing pages have more screen real estate to display their information on.
Backend: Theme polishing
The InvenioRDM theme was refactored and cleaned up, providing better overridability for subthemes and instances. See documentation for further details.
OAI-PMH sets support¶
The OAI-PMH server in InvenioRDM has now been extended with sets support that was missing in earlier implementations.
You can see an example of the set here.
Sets for communities
An OAI-PMH set is automatically created for each public community. This allows any public community to be harvested.
Custom sets
In addition to the sets created for communities, it's also possible for an administrator to create custom sets. A custom set is simply defined by a search query.
Management REST API
The custom OAI-PMH sets can currently be managed via the REST API. A future version will add a user interface to allow an administrator to manage the sets.
See OAI-PMH REST API documentation.
Backend: Flask-Security to Flask-Security-Invenio¶
Invenio Framework has for a long time relied on the Flask-Security module for providing the core authentication and authorization features. Unfortunately, the module has not been maintained for quite some time, and thus we have decided to maintain a private fork named Flask-Security-Invenio of the module ourselves.
We have released Flask-Security-Invenio v3.1.x based on Flask-Security 3.0 as a stripped down version where we have removed features that were not used by Invenio such as e.g. token and basic authentication methods. We decided not to migrate to the community fork named Flask-Security-Too due to a significantly feature scope such as two-factor authentication.
We highly recommend that you use a proper identity and access management solution together with InvenioRDM such as e.g. Keycloak or e.g. ORCID. These systems are specifically focused on providing secure authentication and support the lastest methods such as two-factor authentication.
Backend: Bulk indexing and automatic propagation of updates¶
InvenioRDM now ships with support for bulk indexing (i.e. indexing multiple records in a single indexing request to a search cluster). Bulk indexing is needed for performance reasons when we have to index many records at once. This happens for instance if we update a vocabulary record (e.g. resource type, affiliation, etc.), and as a result have to propagate the changes to related records.
Bulk indexing works by having the application queue a request to index one or more records. A background worker then checks every 10 seconds (via the invenio_records_resources.tasks.manage_indexer_queues task) to see if there are any queued indexing requests, and if so, will kick-off the bulk indexing. The bulk indexing will index up to 500 records at a time.
Backend: Search field transformer¶
We have added basic backend support for parsing and transforming search
queries. This allows us in the future to improve the fields that users can use
in search queries. For instance today, a user will have to write
metadata.title:... to search specifically on the title field. In the future,
using the search field transformer, we're now able to parse the query from the
user and automatically modify and transform the query, so a user can search
on e.g. title:... instead.
The new search field transformer is currently used in the new users/groups
REST API so you can search on fields like name, email,
username and affiliation when looking for users to invite to a
community.
Below is an example on how the search field transformer is used:
from invenio_records_resources.services.records.queryparser import (
QueryParser,
SearchFieldTransformer,
)
class UserSearchOptions(SearchOptions):
# ...
query_parser_cls = QueryParser.factory(
fields=["username^2", "email^2", "profile.full_name^3", "profile.affiliations"],
tree_transformer_factory=SearchFieldTransformer.factory(
mapping={
"affiliation": "profile.affiliations",
"affiliations": "profile.affiliations",
"email": "email",
"full_name": "profile.full_name",
"fullname": "profile.full_name",
"name": "profile.full_name",
"username": "username",
}
),
)
Upgrading to v9.0¶
We support upgrading from v8.0 to v9.0. Please see the upgrade notice.
Maintenance policy¶
InvenioRDM v9.0 is a long-term support (LTS) release which is supported until the next LTS release + 6 months and for minimum 1 year. See our Maintenance Policy.
Requirements¶
InvenioRDM v9.0 supports:
- Python 3.7, 3.8 and 3.9
- PostgreSQL 10+
- Elasticsearch 7
Note that Python 3.6, Elasticsearch 6 and PostgreSQL 9 have all reached end of life and are no longer supported by their respective organisations.